Stroke is a leading cause of death. Stroke care is limited by the availability of specialized medical professionals. In this post, we describe a physician-led stroke unit model established at Baptist Christian Hospital (BCH) in Assam, India. Enabled with qER, Qure’s AI driven automated CT Brain interpretation tool, BCH can quickly and easily determine next steps in terms of treatment and examine the implications for clinical outcomes.
Back
qER at a Stroke unit
Across the world, Stroke is a leading cause of death, second only to ischemic heart disease. According to the the World Stroke Organization (WSO), 13.7 million new strokes occur each year and there are about 80 million stroke survivors globally. In India as per the Health of the Nation’s State Report we see an incidence rate of 119 to 152/100000, and has a case fatality rate of 19 to 42% across the country.
Catering to tea plantation workers in and around the town of Tezpur, the Baptist Christian Hospital, Tezpur (BCH) is a 130-bed secondary care hospital in the North eastern state of Assam in India. This hospital is a unit of the Emmanuel Hospital Association, New Delhi. From humble beginnings, offering basic dispensary services, the hospital grew to become one of the best healthcare providers in Assam, being heavily involved in academic and research work at both national and international levels.
Nestled below the Himalayas, interspersed with large tea plantations, Assamese indigenous population and tea garden workers showcase a prevalence of hypertension, the largest single risk factor of stroke, reportedly between 33% to 60.8%. Anecdotal reports and hospital-based studies indicate a huge burden of stroke in Assam – a significant portion of which is addressed by Baptist Hospital. Recent study showed that hemorrhagic strokes account for close to 50% of the cases here, compared to only about 20% of the strokes in the rest of India.
Baptist Christian Hospital, Tezpur. Source
Challenges in Stroke Care
One of the biggest obstacles in Stroke Care is the lack of awareness of stroke symptoms and the late arrival of the patient, often at smaller peripheral hospitals, which are not equipped with the necessary scanning facilities and the specialists, leading to a delay in effective treatment.
The doctors and nurses of the Stroke Unit at BCH, Tezpur were trained online by specialist neurologists, who in turn trained the rest of the team on a protocol that included Stroke Clinical Assessment, monitoring of risk factors and vital parameters, and other supportive measures like management of Swallow assessment in addition to starting the rehabilitation process and advising on long term care at home. A study done at Tezpur indicated that post establishment of Stroke Unit, there was significant improvement in the quality of life along with reduction in deaths compared to the pre-Stroke Unit phase.
This is a crucial development in Stroke care especially in the low and middle income countries(LMIC) like India, to strengthen the peripheral smaller hospitals which lack specialists and are almost always the first stop for patients in emergencies like Stroke.
This representative image details the acute stroke care pathway. Source
The guidelines for management of acute ischemic stroke involves capturing a non-contrast CT (NCCT) study of the brain along with CT or MRI angiography and perfusion and thrombolysis-administration of rTPA (Tissue Plasminogen Activator) within 4.5 hours of symptom onset. Equipped with a CT machine and teleradiology reporting, the physicians at BCH provide primary intervention for these stroke cases after a basic NCCT and may refer them to a tertiary facility, as applicable. They follow a Telestroke model-in cases where thrombolysis is required, the ER doctors consult with neurologists at a more specialized center and the decision making is done upon sharing these NCCT images via phone-based mediums like WhatsApp while severe cases of head trauma are referred for further management to far away tertiary facilities. There have been studies done on a Physician based Stroke Unit model in Tezpur, that has shown an improvement in treatment outcomes.
How is Qure.ai helping BCH with stroke management?
BCH and Qure have worked closely since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, especially at a time when confirmatory RT-PCR kits were limiting. qXR, Qure’s AI aided chest X-ray solution had proved to be a beneficial addition for identification of especially asymptomatic COVID-19 suspects and their treatment and management, beyond its role in comprehensive chest screening.
AI at BCH
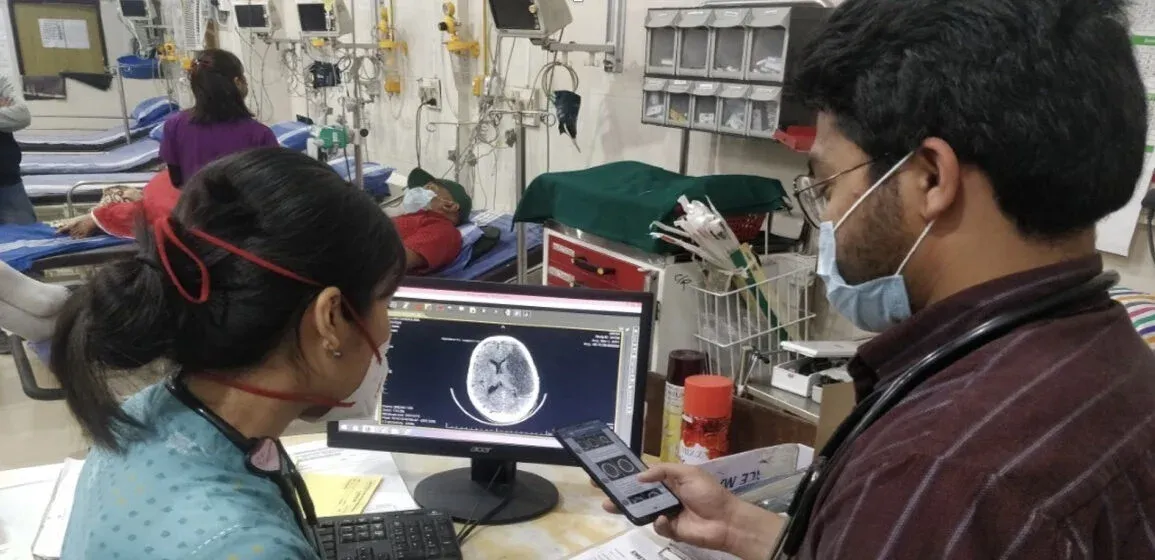
In efforts to improve the workflow of stroke management and care at the Baptist hospital, qER, FDA approved and CE certified software which can detect 12 abnormalities was deployed. The abnormalities including five types of Intracranial Hemorrhages, Cranial Fractures, Mass effect, midline Shift, Infarcts, Hydrocephalus, Atrophy etc in less than 1-2 minutes of the CT being taken. qER has been trained on CT scans from more than 22 different CT machine models, thus making it hardware agnostic. In addition to offering a pre-populated radiology report, the HIPAA compliant qER solution is also able to label and annotate the abnormalities in the key slices.
Since qER integrates seamlessly with the existing technical framework of the site, the deployment of the software was completed in less an hour along with setting up a messaging group for the site. Soon after, within minutes of taking the Head CT, qER analyses were available in the PACS worklist along with messaging alerts for the physicians’ and medical team’s review on their mobile phones.
The aim of this pilot project was to evaluate how qER could add value to a secondary care center where the responsibility for determination of medical intervention falls on the physicians based on teleradiology report available to them in a span of 15-60 minutes. As is established with stroke care, every minute saved is precious.
Physician using qER
At the outset, there were apprehensions amongst the medical team about the performance of the software and its efficacy in improving the workflow, however, this is what they have to say about qER after 2 months of operation:
“qER is good as it alerts the physicians in a busy casualty room even without having to open the workstation. We know if there are any critical issues with the patient” – Dr. Jemin Webster, a physician at Tezpur.
He goes on to explain how qER helps grab the attention of the emergency room doctors and nurses to critical cases that need intervention, or in some instances, referral. It helps in boosting the confidence of the treating doctors in making the right judgement in the clinical decision-making process. It also helps in seeking the teleradiology support’s attention into the notified critical scans, as well as the scans of the stroke cases that are in the window period for thrombolysis. Dr. Jemin also sees the potential of qER in the workflow of high volume, multi-specialty referral centers, where coordination between multiple departments are required.
The Way Ahead
A technology solution like qER can reduce the time to diagnosis in case of emergencies like Stroke or trauma and boosts the confidence of Stroke Unit, even in the absence of specialists. The qER platform can help Stroke neurologists in the Telestroke settings access great quality scans even on their smartphones and guide the treating doctors for thrombolysis and further management. Scaling up this technology to Stroke units and MSUs can empower peripheral hospitals to manage acute Stroke especially in LMICs.
We intend to conduct an observational time-motion study to analyze the Door-to- Needle time with qER intervention via instant reports and phone alerts as we work through the required approvals. Also in the pipeline is performance comparison of qER reporting against the Radiologist report as ground truth along with comparison of clinical outcomes and these parameters before and after introduction of qER into the workflow. We also plan to extend the pilot project to Padhar Mission Hospital, MP and the Shanthibhavan Medical Center, Simdega, Jharkhand.
Qure team is also working on creating a comprehensive stroke platform which is aimed at improving stroke workflows in LMICs and low-resource settings.