Every day, countless people rise out of chairs or beds and wince at the pain in their lower backs. Lower back pain is considered the leading cause of disability in 160 countries. It is also an indicator of potential musculoskeletal (MSK) conditions.
Back
In 2022, the World Health Organisation estimated that 21% of the world's population suffered from musculoskeletal ailments. MSK-related issues limit movement and flexibility and are a key factor in disability, early retirement, poorer well-being, and a diminished ability to contribute to or participate in societal activities.
Musculoskeletal fractures are a common occurrence in clinical practice, with over 2 million fractures occurring annually in the United States alone. Meanwhile, the UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and Sweden (EU6 nations) see 2.7 million fractures taking place yearly. The currently associated healthcare expenditure is €37 billion; it is projected to increase to €47 billion (an increase of 23%) by 2030 and a staggering €77 billion by 2050.
Detecting musculoskeletal fractures is essential for providing appropriate treatment, as untreated fractures can lead to long-term disabilities. Diagnosing fractures typically involves X-rays, allowing doctors to visualize the bone and determine the extent of the injury. Emergency physicians must usually review MSK radiographs to determine a treatment approach before radiologists can review the images and provide a formal report.
Medical imaging has revolutionised healthcare by providing non-invasive diagnostic tools. But the shortage of radiologists worldwide, along with the growing number of studies and images per study, have proportionately increased the workloads of radiologists as well. It has resulted in the possibility of lower efficiency and a higher risk of errors that accompany burnout. The most common diagnostic mistakes made by clinicians interpreting musculoskeletal radiographs involve missed fractures. These errors cause treatment delays, avoidable medical costs, legal issues, and morbidity that could have been prevented.
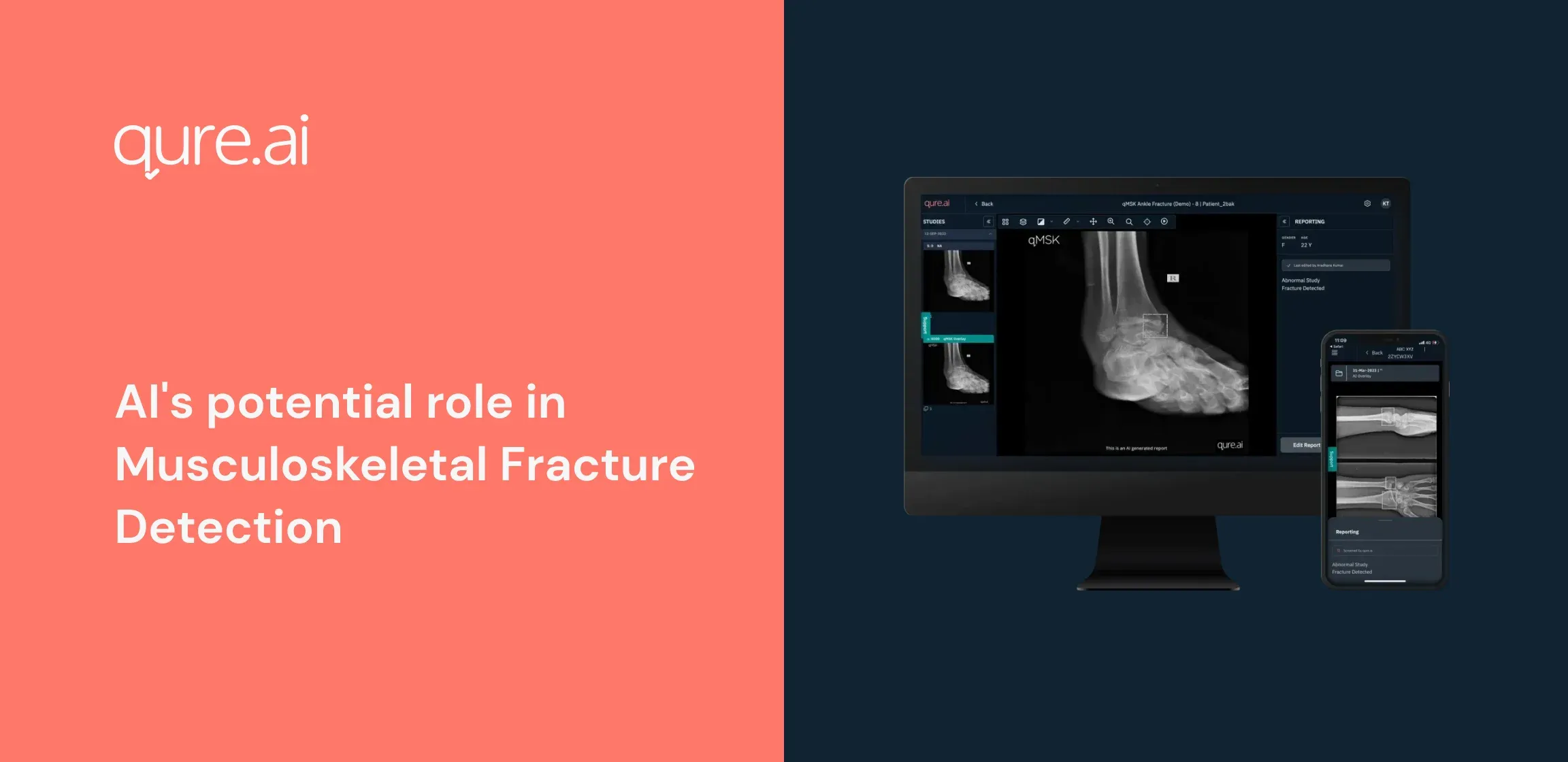
This is where Artificial Intelligence has a role to play. AI algorithms can be trained to recognize patterns in X-ray images that may indicate the presence of a fracture. These algorithms can also be used to classify the type of fracture and predict the likelihood of it healing successfully. AI tools like qMSK by Qure.ai have the potential to improve the accuracy and efficiency of musculoskeletal imaging diagnosis, deliver imaging results to clinicians and provide emergency physicians with more accurate imaging information at the time of patient contact, improving patient care and triage.
It should be emphasized that the quality and quantity of the training data dramatically influence the accuracy of AI algorithms for fracture detection. Therefore, continuous efforts to collect and annotate large radiograph datasets are imperative to enhance the precision of these algorithms. In addition, radiologists possess the expertise to identify and incorporate suitable AI software to assist non-radiologists in various situations. Moreover, they are equipped to provide necessary oversight and training to other medical professionals regarding using AI tools for fracture detection.
The potential impact of an AI tool augmenting the efforts of healthcare stakeholders to identify MSK fractures cannot be emphasised enough. In particular, emergency physicians could benefit significantly from AI-powered imaging technology, which can act as a secondary pair of eyes or reader, providing clinicians with more accurate imaging information at the time of patient contact. The AI tool can also bolster their original diagnosis or even urge them to revisit their interpretation of the image before treating patients.
In essence, the AI's input, combined with the clinical examination and the physician's own judgment, can help render a more correct diagnosis and treatment approach the first time. It can empower physicians to treat patients based on more accurate imaging information, help triage patients effectively and render a more correct diagnosis and treatment approach the first time, saving valuable time in the treatment pathway.
While research into using AI tools for musculoskeletal fracture detection is still nascent, it does have tremendous potential to impact stakeholders across the healthcare value chain. Therefore, it is imperative that the use of AI and deep learning solutions for musculoskeletal issues be pursued with due perseverance and rigor.
References: